We engage people to look at their work differently and coach them to continuously improve what they do. With our Lean Coaching services we support you to streamline your operations or production and develop a set of standards tailored to your organization.
Our suite of Lean coaching and consulting services are designed to support the improvement of a wide range of organizational needs, from specific problem-solving workshops to more complex transformation initiatives. Here’s an overview of each approach:
Duration: 5 to 10 days
Description: A Kaizen event is a focused, short-term project aimed at improving a specific area within an organization. It brings together cross-functional teams to identify issues, brainstorm solutions, and implement changes quickly, typically within a week.
This method relies on the collective talents and insights of the team, emphasizing incremental, continuous improvements for lasting organizational efficiency and effectiveness.
Directly address and solve a particular problem, streamlining processes, services or production.
Organizations can expect to see improvements in performance and efficiency by 5-10% or more, directly impacting productivity and operational costs.
Duration: 3-6 months
Description: This program leverages DMAIC, a data-driven problem solving method used for reducing variability and enhancing product or service quality. It stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, offering a structured methodology for making significant, measurable improvements in value streams and quality performance.
Full or short cycle DMAIC offers a structured, phase-driven approach for an in-depth problem analysis and solution implementation.
To systematically reduce process, product or service variability and enhance quality, focusing on measurable, long-term improvements.
By focusing on eliminating variability, organizations can achieve substantial benefits, with improvements often exceeding 25-30%. This approach is particularly effective for projects that require a deep, analytical understanding of the problem to drive long-term, sustainable improvements.
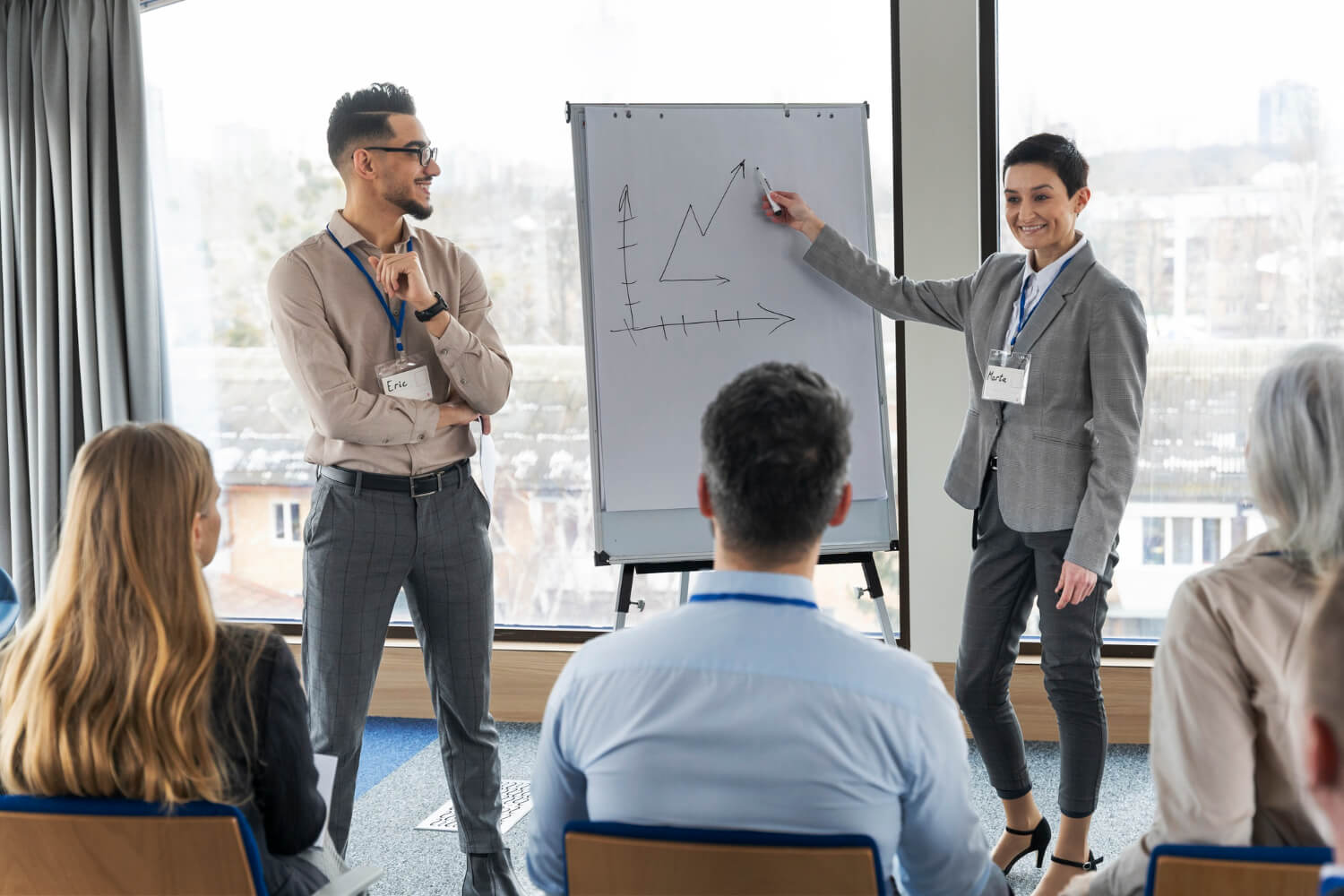

A Lean consultant who understands how to help teams and organizations improve their operations or production.
Create the conditions for success
Create a clear vision and objective for the team
Develop an 360° picture to ensure that actions are linked to the strategy
Understand what is really happening at every level (on the floor and in the office)
Understand the current situation and to build a strong relationship with people
Create a common understanding of the problems and the solutions to solve them
Master observation, investigation and analytical skills
They are able to break down a problem making it solvable
Master various problem solving tools and analytical methods
Structure project or program life cycle
Have a deep understanding of Lean and / or Six Sigma
Master Lean tools to help people work together
Maximise the potential of people
Understand how people learn and change to be able to convince them
Supports team members develop a problem solving and continuous improvement mindset

The PDCA cycle, standing for Plan-Do-Check-Act, is a four-step management method used for continuous improvement of processes and products. It’s a cyclical strategy that begins with planning, implementing the plan, checking the results, and taking action to further refine and improve the process, fostering a culture of ongoing optimization and efficiency.
A Kaizen event is a focused, short-term project aimed at improving a specific area within an organization. It brings together cross-functional teams to identify issues, brainstorm solutions, and implement changes quickly, typically within a week. This method relies on the collective talents and insights of the team, emphasizing incremental, continuous improvements for lasting organizational efficiency and effectiveness.
DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a data-driven quality strategy used to improve processes. This methodological approach allows teams to identify inefficiencies in a process, measure performance to quantify the problem, analyze data to identify the cause, implement improvements, and control the new process to ensure continued success. It’s especially effective for projects aiming at reducing variability and enhancing quality.
The A3 process is a structured problem-solving and continuous improvement approach, which encourages a concise and impactful way of making changes by using a single A3-size paper. This methodology encompasses problem identification, root cause analysis, solution ideation, implementation planning, and review, facilitating clear communication and decision-making. It’s particularly valued for its simplicity, focus on teamwork, and effectiveness in driving meaningful change within organizations.
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a lean management tool used to visualize the steps needed to take from product creation to delivering it to the end-customer. By laying out the entire process visually, organizations can identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. VSM helps in understanding the flow of materials and information as a product makes its way through the value stream, making it a powerful tool for identifying bottlenecks and eliminating waste to optimize the overall process flow.
5S is a systematic approach to workplace organization, derived from five Japanese terms: Seiri (Sort), Seiton (Set in order), Seiso (Shine), Seiketsu (Standardize), and Shitsuke (Sustain). This method helps businesses streamline their environments, reduce waste, and optimize productivity by maintaining an orderly workspace. Through its phases, 5S improves safety, efficiency, and creates a strong foundation for continuous improvement, making it a fundamental strategy for operational excellence in various industries.
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Dies) is a process improvement technique that reduces the time required to change from one product to the next. It aims to minimize equipment setup times to less than 10 minutes. By analyzing each step of a setup and separating internal from external activities, organizations can streamline transitions, increase flexibility, and reduce downtime. This lean manufacturing tool enhances production efficiency and allows for more responsive and cost-effective operations.
SIPOC is a tool used in process improvement that outlines the Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers involved in a process. This high-level overview helps identify critical elements of a process improvement project, ensuring that changes are aligned with customer requirements and organizational goals. It’s an effective way to visualize and understand the scope and stakeholders of a process before delving into more detailed analysis.
The Pareto Analysis, also known as the 80/20 rule, is a technique used for decision-making based on the idea that 80% of effects come from 20% of causes. It helps in identifying and prioritizing problem areas or opportunities by highlighting the most significant factors. This method is widely used across various industries for quality control, process improvement, and resource allocation, allowing teams to focus their efforts on the changes that will have the most significant impact.
The 5 Whys is a problem-solving method that encourages teams to get to the root cause of an issue by asking “Why?” five times. This technique, simple yet powerful, helps peel away layers of symptoms to uncover the fundamental cause of a problem. It’s particularly effective for troubleshooting, quality improvement, and understanding the underlying reasons behind a challenge, promoting a deeper insight into operational issues and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and critical thinking within organizations.
The Ishikawa Diagram, also known as the Fishbone Diagram, is a tool used to systematically identify and present all possible causes of a problem. It helps teams visualize the relationship between a specific issue and its potential causes, categorizing them into broader factors, often including people, processes, and technology. This analysis aids in pinpointing the root causes of problems, facilitating effective problem-solving strategies and promoting a thorough understanding of complex issues within project management and quality control processes.
Statistical problem solving is a methodical approach that uses statistical tools and techniques to identify, analyze, and solve problems. It involves collecting data, analyzing it to find patterns or anomalies, and making decisions based on statistical evidence. This approach helps in understanding the variability and root causes of problems, enabling organizations to make more informed, data-driven decisions. It’s widely applied in quality control, process improvement, and operational efficiency, fostering a culture of evidence-based decision making and continuous improvement.
In a Lean Six Sigma context, hypothesis testing is a critical tool used to support data-driven decision-making. It helps in validating improvements by statistically proving or disproving assumptions about process changes. For example, when implementing a new process to reduce waste, hypothesis testing can confirm whether the change genuinely leads to statistically significant improvements. This approach ensures that decisions are not based on assumptions or anecdotal evidence but are backed by rigorous statistical analysis, aligning with Lean Six Sigma’s focus on eliminating defects and variability in processes.